Innovations in Glass Technology: How Custom Glass Solutions Are Shaping the Future of Scientific Research
https://moores-glass.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/cdc-UBJJuAOv9os-unsplash-1024x720.jpg 1024 720 Matthew Morris Matthew Morris https://secure.gravatar.com/avatar/09048644f0c2340325fc98c2460d4a4f?s=96&d=mm&r=gDiscover the latest innovations in glass technology and how custom glass solutions from Moore’s Glass are revolutionising scientific research.
Introduction
Glass technology has evolved significantly and is integral to various scientific fields. As the demand for precision and specialised equipment increases, innovations in glass technology are paving the way for groundbreaking discoveries. This blog explores these advancements and highlights how custom glass solutions from Moore’s Glass are shaping the future of scientific research.
The Evolution of Glass Technology
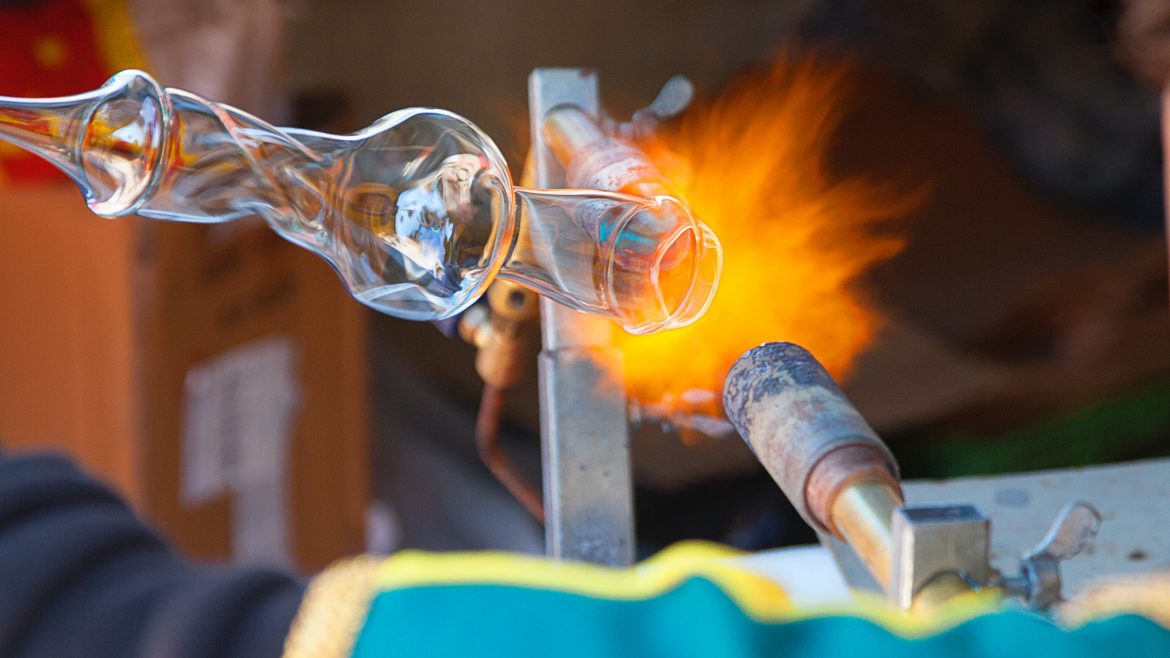
The journey of glass technology is marked by continuous improvement and innovation. From simple glassware to highly specialised scientific instruments, glass has always been crucial in advancing scientific knowledge. The evolution of manufacturing techniques and material science has enhanced the properties and applications of glass, making it indispensable in modern research. Today, glass technology is at the forefront of scientific exploration, offering unparalleled precision and durability.
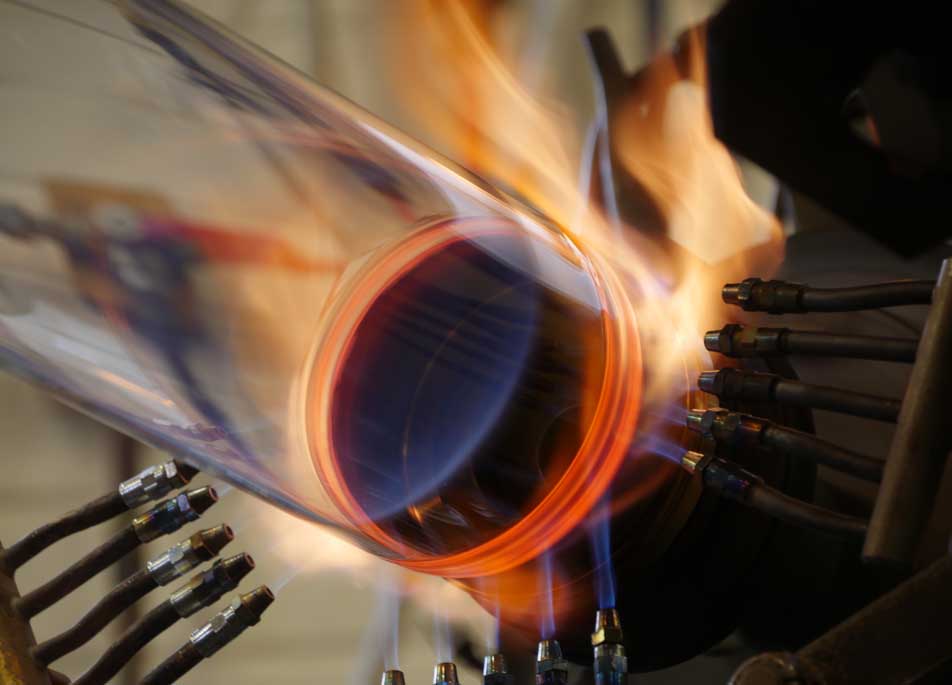
 Key Innovations in Glass Technology
Key Innovations in Glass Technology
Recent advancements in glass technology have introduced high-strength glass that can withstand extreme conditions and stress. Ultra-thin glass has also emerged, offering flexibility and transparency essential for sophisticated scientific instruments. Additionally, smart glass, which can change its properties in response to external stimuli, is revolutionising research environments by providing adaptable solutions for various experimental needs. These innovations have significantly broadened the scope of scientific research, enabling new methodologies and applications.
Custom Glass Solutions for Scientific Research
In scientific research, the need for precision and specialised equipment is paramount. Custom glass solutions cater to these needs by providing tailored glassware and instruments to meet specific research requirements. Precision glassware ensures accurate measurements and results, while specialised lab equipment can withstand unique conditions encountered in various experiments. Custom glass instruments, such as intricate microscope lenses, enhance the
capabilities of scientific investigations, allowing researchers to achieve greater accuracy and reliability in their findings.
Benefits of Custom Glass Solutions in Research
The benefits of custom glass solutions in scientific research are extensive. Enhanced durability ensures that glassware and instruments can withstand rigorous experimental conditions without compromising performance. Improved accuracy and precision, achieved through meticulous manufacturing processes, contribute to consistent and reliable results. The versatility of custom glass solutions allows researchers to explore a wide range of applications, from chemistry and biology to physics and engineering. This adaptability is crucial in facilitating innovative research and experimentation.
Case Studies: Impact of Glass Innovations on Scientific Discoveries
Innovative glass solutions have been pivotal in enabling groundbreaking experiments and discoveries. For instance, custom glass advancements have facilitated new microscopy techniques, allowing scientists to observe biological processes at unprecedented resolutions. Breakthrough experiments in particle physics and materials science have been made possible through specialised glass apparatus. These case studies highlight the transformative impact of glass innovations on scientific research and underscore the importance of custom glass solutions in advancing knowledge.
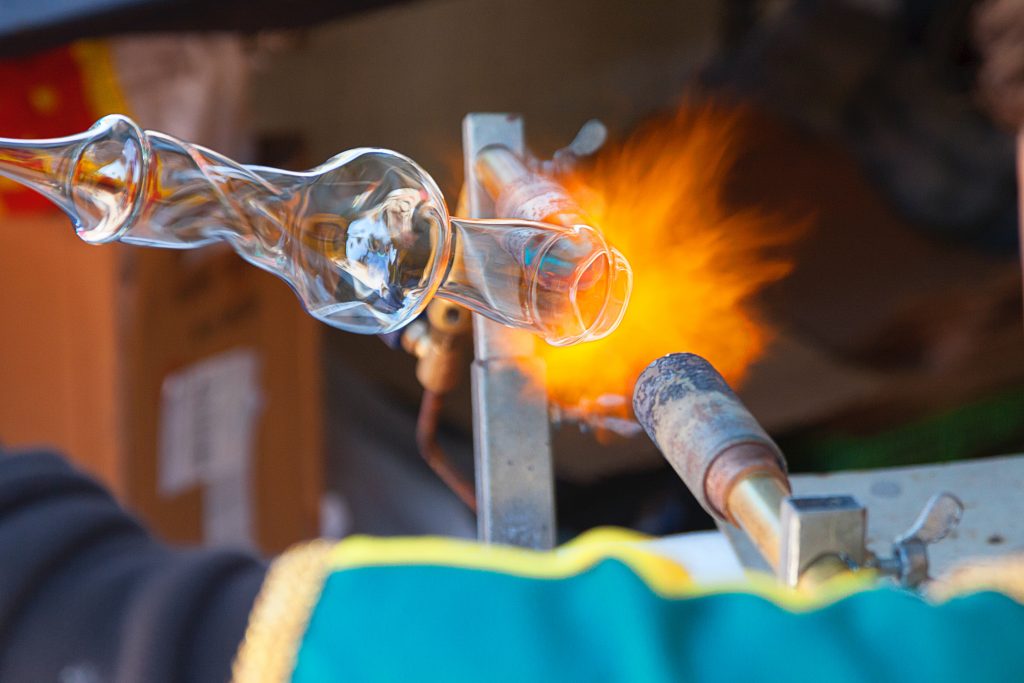
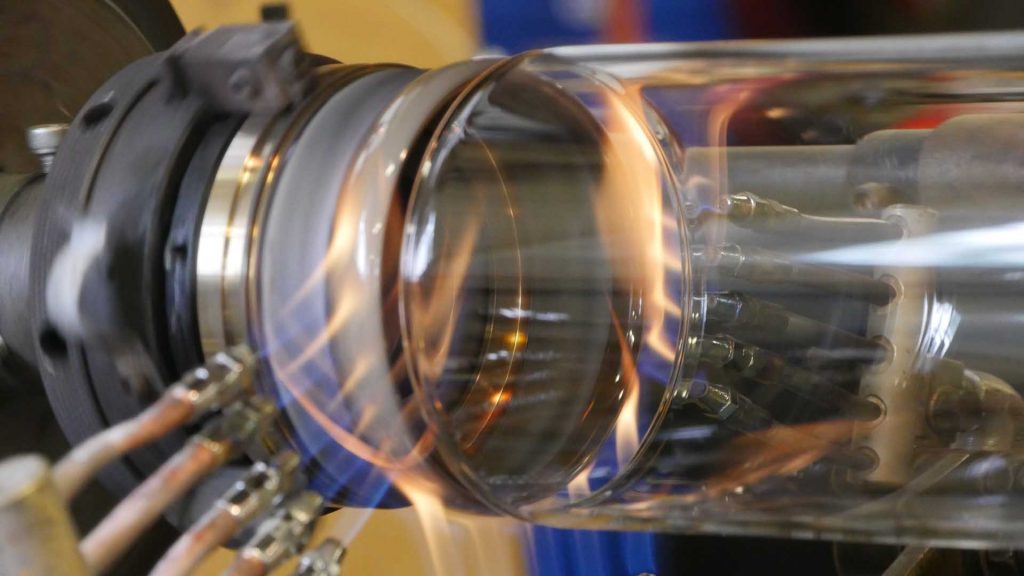
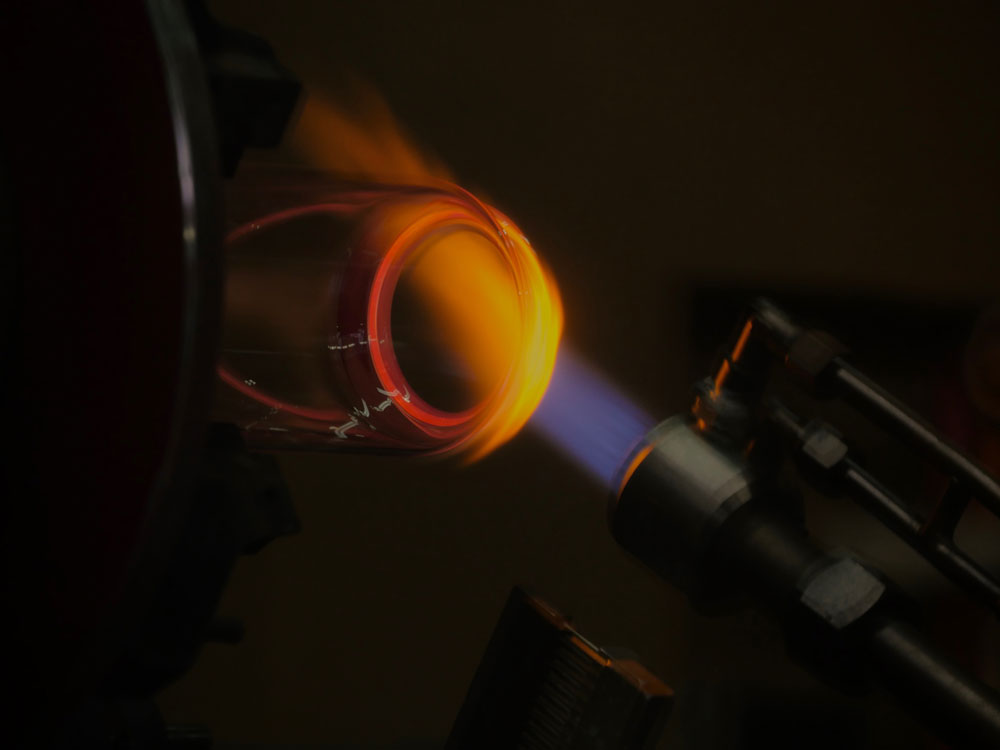
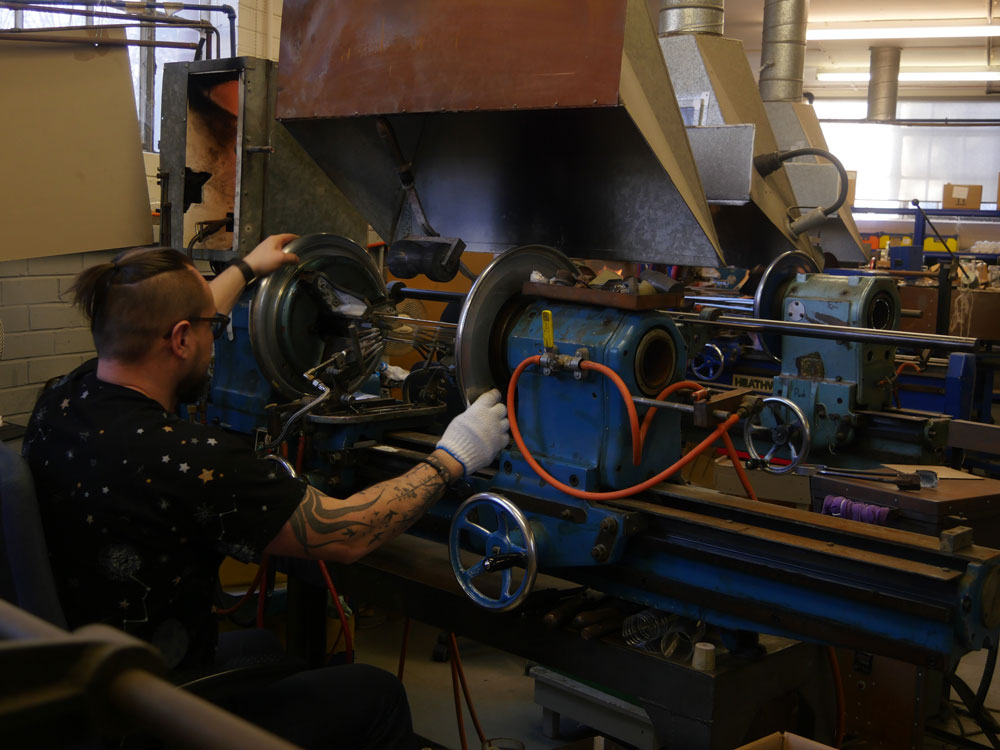
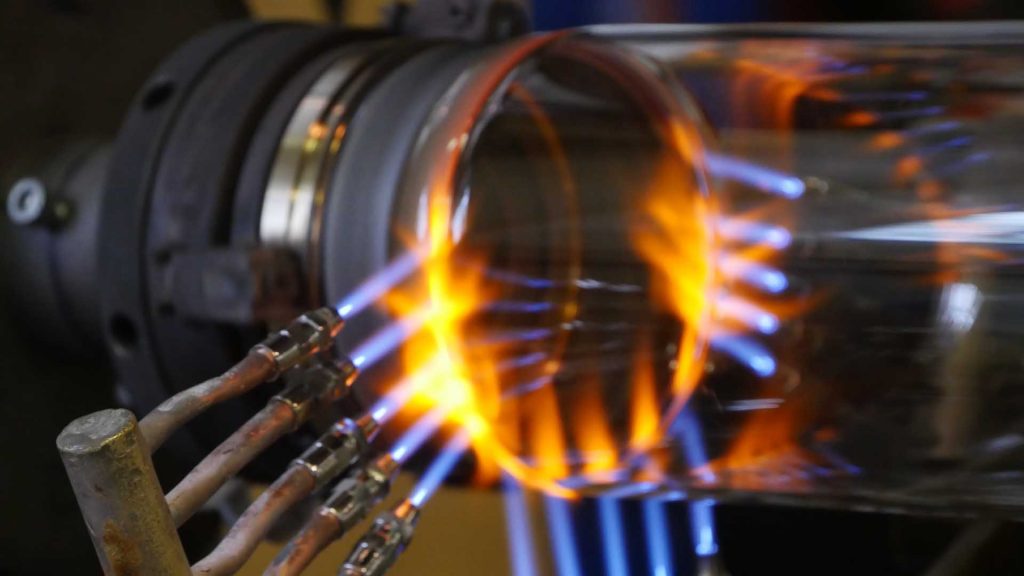
Challenges and Solutions in Custom Glass Fabrication
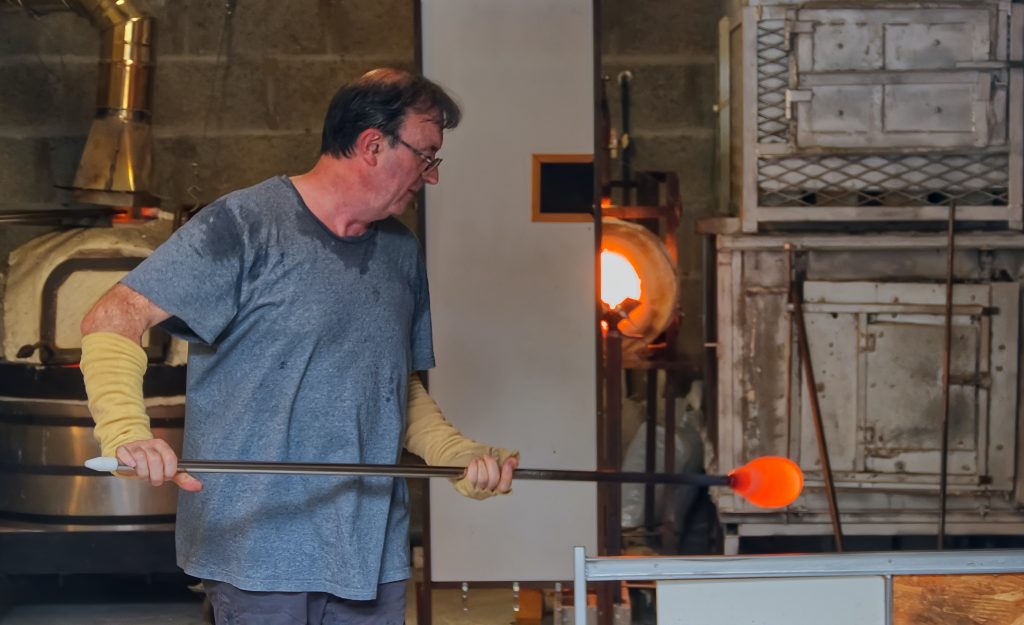
Custom glass fabrication presents several challenges that need to be addressed to meet the specific needs of scientific research. Quality control is crucial in maintaining the high standards required for scientific use. At Moore’s Glass, we tackle these challenges through rigorous quality assurance processes and close collaboration with researchers. By understanding each project’s unique requirements, we are able to deliver custom glass solutions that meet the highest standards of precision and durability.
The Role of Advanced Glass in Future Technologies
Advanced glass technology is set to play a pivotal role in future technological advancements. In nanotechnology, custom glass solutions are essential for creating nanoscale structures and devices. In biotechnology and medical research, glass innovations enable the development of advanced diagnostic tools and treatment methods. The adaptability and precision of advanced glass make it a cornerstone of future scientific breakthroughs, driving innovation across various fields.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability of Glass Innovations
Sustainability is a key consideration in the development of advanced glass products. Eco-friendly manufacturing practices are being adopted to reduce the environmental impact of glass production. Additionally, the recyclability of advanced glass products contributes to a circular economy, ensuring that glass remains a sustainable material choice for scientific and industrial applications. At Moore’s Glass, we are committed to implementing sustainable practices that minimise environmental impact while delivering high-quality products.
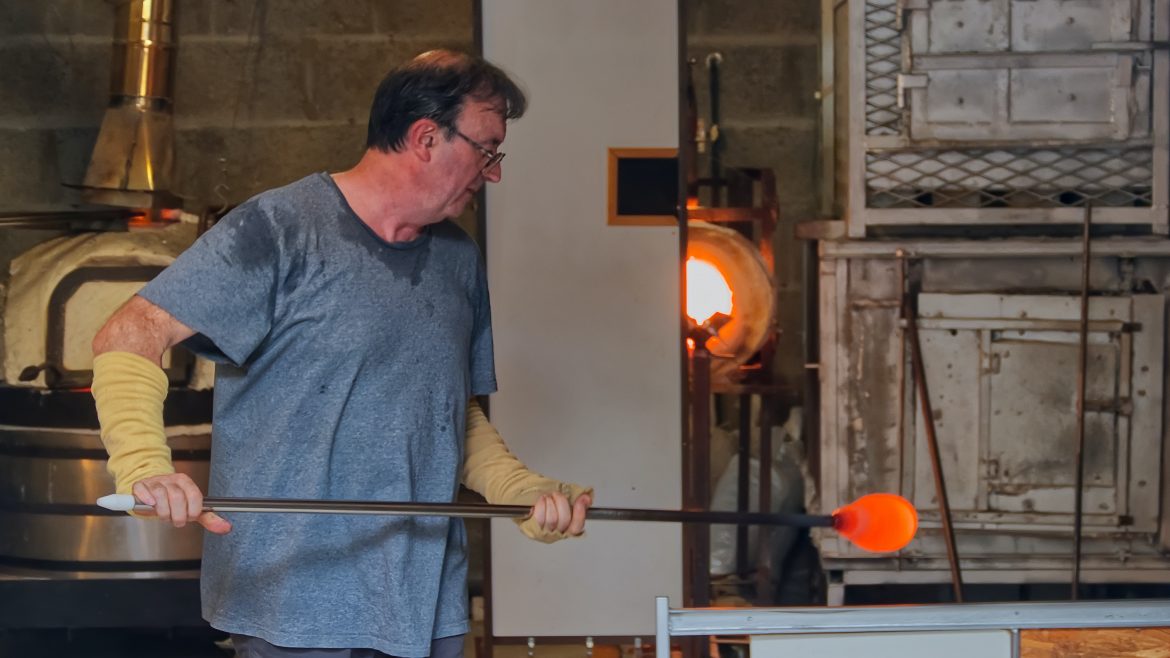
Moore’s Glass: Leading the Way in Glass Innovations
Moore’s Glass is at the forefront of glass technology innovation, providing cutting-edge solutions tailored to scientific research needs. Our commitment to quality and innovation drives us to deliver custom glass products that meet the highest standards of precision and durability. Our success stories reflect our dedication to supporting scientific advancements through innovative glass solutions, making us a trusted partner in the research community. By collaborating with researchers and understanding their unique needs, we can contribute significantly to their success and the advancement of scientific knowledge.
Conclusion
Innovations in glass technology are revolutionising scientific research, offering new possibilities for discovery and advancement. Custom glass solutions enhance research tools’ accuracy, durability, and versatility, enabling scientists to push the boundaries of knowledge. At Moore’s Glass, we are proud to contribute to this exciting future by providing top-tier custom glass products that support and inspire scientific excellence.